Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Search engine optimization (SEO) is aimed at creating websites such that they can be found by search engines when searching for a certain topic. In addition, the hits are to appear near to the top of the list, if possible. SEO also focuses on the user is in the focus. This means that the contents of a website should answer the questions of the user in his search situation as comprehensively as possible. For this reason, contents must be structured such that they can be searched and indexed by search engines.
HINWEIS: It is dealt with the contents of websites only, technical factors (e.g. loading time of the website, accessibility of the server, mobile optimization, etc.) are not considered.
Instructions for SEO-compliant Writing
Structure the Texts
The text should answer questions of a user relating to a closely defined topic. Well-structured contents influence the ranking of search engines (see also Section “Text Style”).
Use Keywords
Keywords are search terms entered by users into search engines to find certain information. A keyword is a term that describes the topic of a website.
This is how it works: Identify keywords
To identify suitable keywords, put yourself in the user’s position. It is important to choose keywords that are as specific as possible. Ask yourself the following questions:
- What does the user search for?
- Which search terms might be entered into the search engine by the user to get to your website?
- Which terms may users search for in this context?
Example: Website of the “Mechanical Engineering” program
Possible keywords are: Studying mechanical engineering, bachelor’s program of mechanical engineering, mechanical engineering in Karlsruhe / at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
NOTE: Helpful tools for the identification of keywords:
- Google Trends: Indicates the search frequency of a term.
- Keyword-tools.org: Displays other relevant search terms for a keyword.
- - Automatic completing in the google search area: Google proposes the most frequently used search terms.
This is how it works: Position the keywords properly
Position the keyword at different points in the text on the website. The following list provides an overview of the positions at which keywords can be placed reasonably in the text:
- In titles (H1) and subtitles
- In page titles and descriptions
- Homogeneously distributed in the running text
- In Links
- In figure captions and ALT-text
- in Video subtitles
NOTE: Do not use the keyword too often in the text. Users and search engines might consider this “spam.”
Optimize the Representation of the Search Result
When the user enters a keyword into the search engine, the websites are listed with a so-called snippet. A snippet consists of a title, a short description and the URL.
Snippets often are the first points of contact of users with the websites and decide on whether the website is accessed or not. Snippets should arouse interest and make the user click the website.
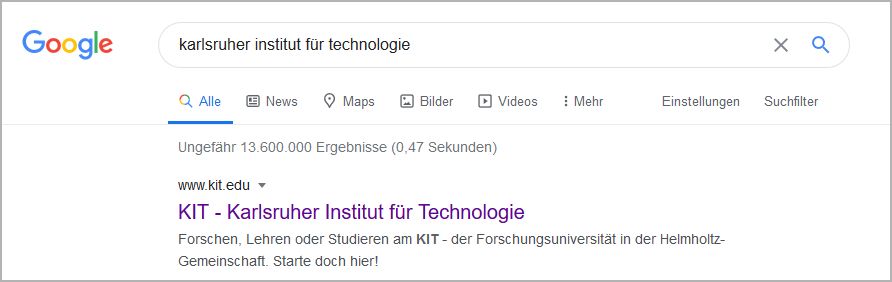
Edit the Title
The element “title” contains the page title and consists of a maximum of 60 characters.
NOTE: The title of projects of organizational units consists of the page title and the browser title prefix (see documentation SCC). In the search result it is partly represented as a breadcrumb.
This is how it works: Edit the page title in OpenText
- Click Rahmenseite bearbeiten (edit frame page)
- Select the item Einstellungen (settings)
- Select the item weitere Einstellungen (other settings)
- Enter the page title under „Überschrift der Seite“ (page title)
This is how it works: Edit the browser title prefix in OpenText
- Open the SmartEdit-Seite
- Click Projektvorgaben (project requirements) under Projekteinstellungen und –vorgaben (project settings and requirements)
- Enter the prefix in the field Browsertitel-Präfix (browser title prefix).
Edit the Description (Meta Description)
The “meta description” element provides a short overview of the contents of the website and should not contain more than about 150 characters, including blanks.
This is how it works: Edit meta description in OpenText
- Click Rahmenseite bearbeiten (edit frame page)
- Select the item Einstellungen (settings)
- Enter a short description of the website in the field “Meta Description, Beschreibung für diese Seite” (meta description, description of this page)
- Contents of the website in brief
- 150 characters (including blanks) at the maximum
NOTE:If no text is entered in the “meta description,” Google uses the first approx. 150 characters of the text on the website and automatically generates a snippet that is displayed in the list of search results. As a rule, such snippets do not arouse the interest of the user.
Optimize Images for Search Engines
The ranking of search results is influenced positively by completing the meta data of an image and entering a keyword.
- Store the image under a file name that contains the keyword.
- Generate an Alt-Text that contains the keyword in OpenText. The Alt-Text describes the image contents and is displayed when the image is not uploaded or a screen reader is used.
- Add an image title that contains the keyword.
Use Speaking URLs
If possible, use “speaking URLs,” as these are evaluated positively by search engines and the user immediately knows what the website is about. Speaking URLs contain information on the topic or the contents of the linked website.
- Generate URLs that contain the keywords.
- Avoid special characters, separate words by hyphens.
- Avoid capitalization.
Example:
- Write “zu den Studiengangsinformationen“ (to information on study programs) instead of “Hier klicken“ (click here).
- www.kit.edu/studiengang/maschinenbau (www.kit.edu/program/mechanical engineering) instead of www.kit.edu/8403.php
